Digital Image Correlation
Main Content
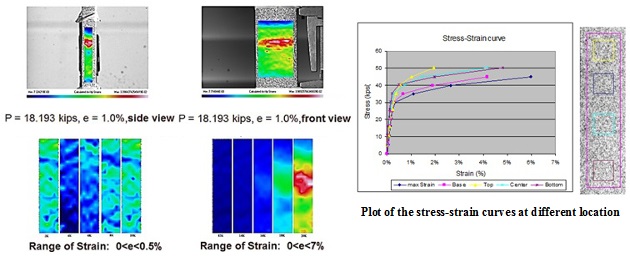
Digital image correlation (DIC) of speckle patterns has been used extensively to measure displacement components and deformation gradients of an object surface due to deformation over three decades. It originated from the use of laser speckle which can be found in many types of coherent imagery. The digital image correlation method was pioneered by Dr. Chu and other researchers at the University of South Carolina in the early 1980s. This correlation technique is currently grabbing intention in the non-destructive evaluation engineering field. At present time, digital cameras and computers are improved tremendously to implement the DIC method in many engineering applications.
Industries served
- Aerospace: composite & advanced material studies, structural loading studies
- Automotive: manufacturing quality analysis & FEM confirmation
- Microelectronics: thermal expansion, PCB NDT & alignments
- Composites Manufacturing: quality control, failure analysis, material & structural properties
- Metal Forming: forming limit measurements
- Biomechanics: bone & tissue strains
- Civil Engineering: road materials analysis, soil loading
Common uses include
- Materials characterization of metallics, composites, ceramics
- Thermal Expansion Measurements
- FEM confirmation & boundary condition checking
- Fracture mechanics and Estimating stability
- Dimensioning components
- Examining non-linear deformation behavior
- Characterizing creep and aging processes
- High-speed deformation & strain measurements



